在 Spring 环境中,如果需要在 Bean 自动装配(属性都注入 ok)完成后进行自定义操作,通常只需要实现接口 InitializingBean,在 afterPropertiesSet 方法中执行操作即可。
在这个接口回调时,Bean 中所有的属性已经注入完成了。比如在 Bean 初始化完成后添加一段 log:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12@Component
public class MyBean implements InitializingBean {
private Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyBean.class);
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
log.info("=======>afterPropertiesSet");
}
}
项目启动后可以看到 log 输出:
INFO com.cml.chat.lesson.lesson2.MyBean - =======>afterPropertiesSet这样的实现方式适合单独的 Bean,如果有多个 Bean 都具有一样的业务逻辑,那么抽象出一个共同类出来即可。
所有的类都继承这个抽象类,但是这样的方式代码入侵大,不太适合用于框架类的项目和共通业务逻辑处理。
那么如何更优雅的在 Bean 初始化前后自定义进行处理呢?这时候 BeanPostProcessor 就派上用场了
BeanPostProcessor
BeanPostProcessor 接口提供了以下方法:
- postProcessBeforeInitialization:在 Bean 初始化回调前调用
- postProcessAfterInitialization:在 Bean 初始化回调完成后进行调用,而且会在 afterPropertiesSet 方法回调之后
两个方法可以在 Bean 初始化回调前后进行处理,而且使用也非常简单,只需要实现 BeanPostProcessor 接口就可以在 Bean 初始化回调前后进行处理其他业务逻辑。这里做个简单的使用示例
实战
先定义好 IMyBean 接口,提供 setCustomValue、getCustomValue 两个方法,当所有 IMyBean 对象 getCustomValue 获取数据为空时,自动设置 customValue 为默认值 “defaultValue”:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20public interface IMyBean {
void setCustomValue(String v);
String getCustomValue();
}
定义好 MyBean 实现 IMyBean 接口:
@Component
public class MyBean implements IMyBean {
private String customValue;
public String getCustomValue() {
return customValue;
}
public void setCustomValue(String customValue) {
this.customValue = customValue;
}
}实现BeanPostProcessor接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23@Component
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
private Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyBeanPostProcessor.class);
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof IMyBean) {
log.info("=======>postProcessAfterInitialization");
IMyBean mybean = (IMyBean) bean;
if (mybean.getCustomValue() == null) {
mybean.setCustomValue("defaultValue");
}
}
return bean;
}
}运行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18@SpringBootApplication()
public class Application {
private static Logger log=LoggerFactory.getLogger(Application.class);
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SpringApplication springApplication = new SpringApplication(Application.class);
// 非web环境
springApplication.setWebEnvironment(false);
ConfigurableApplicationContext application = springApplication.run(args);
MyBean mybean = application.getBean(MyBean.class);
log.info("getCustomValue:"+mybean.getCustomValue());
}
}
log:
com.cml.chat.lesson.lesson2.Application - getCustomValue:defaultValue
输出:com.cml.chat.lesson.lesson2.Application - getCustomValue:myCustomValue这样简单的 BeanPostProcessor 就实现了,那么为什么只要实现 BeanPostProcessor 接口就可以了?
Spring 是如何识别 BeanPostProcessor 的呢?那么这时候该来剖析下 BeanPostProcessor 实现原理了
BeanPostProcessor 原理解析
在 Spring 中,所有的 Bean 都是通过 BeanFactory 进行管理的,Spring Boot 中使用的是 DefaultListableBeanFactory。
可以从以下代码获取 Spring Boot 使用的 BeanFactory1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19@SpringBootApplication()
public class Application {
private static Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Application.class);
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SpringApplication springApplication = new SpringApplication(Application.class);
// 非web环境
springApplication.setWebEnvironment(false);
ConfigurableApplicationContext application = springApplication.run(args);
log.info("beanFactory===>" + application.getBeanFactory().getClass());
application.close();
}
}
输出log:
com.cml.chat.lesson.lesson2.Application - beanFactory===>class org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory
说明:可以看出BeanFactory默认实现类是:DefaultListableBeanFactory当获取 Bean 时,都是通过调用 BeanFactory.getBean 方法获得的。在 SpingBoot 中 BeanFactory 默认使用的是 DefaultListableBeanFactory。
知道了 BeanFactory 就相当于找到了所有 bean 相关的入口。那么剩下的就该来剖析下 BeanPostProcessor 实现原理了说下一个万能的原理查看方法,只要在对应的调用地方添加断点,当断点进入后就可以看到整个方法调用链,这样就可以知道整个流程是如何运作了。
就从上面的例子来说在 MyBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization 方法中添加断点,Debug 运行后可得到如下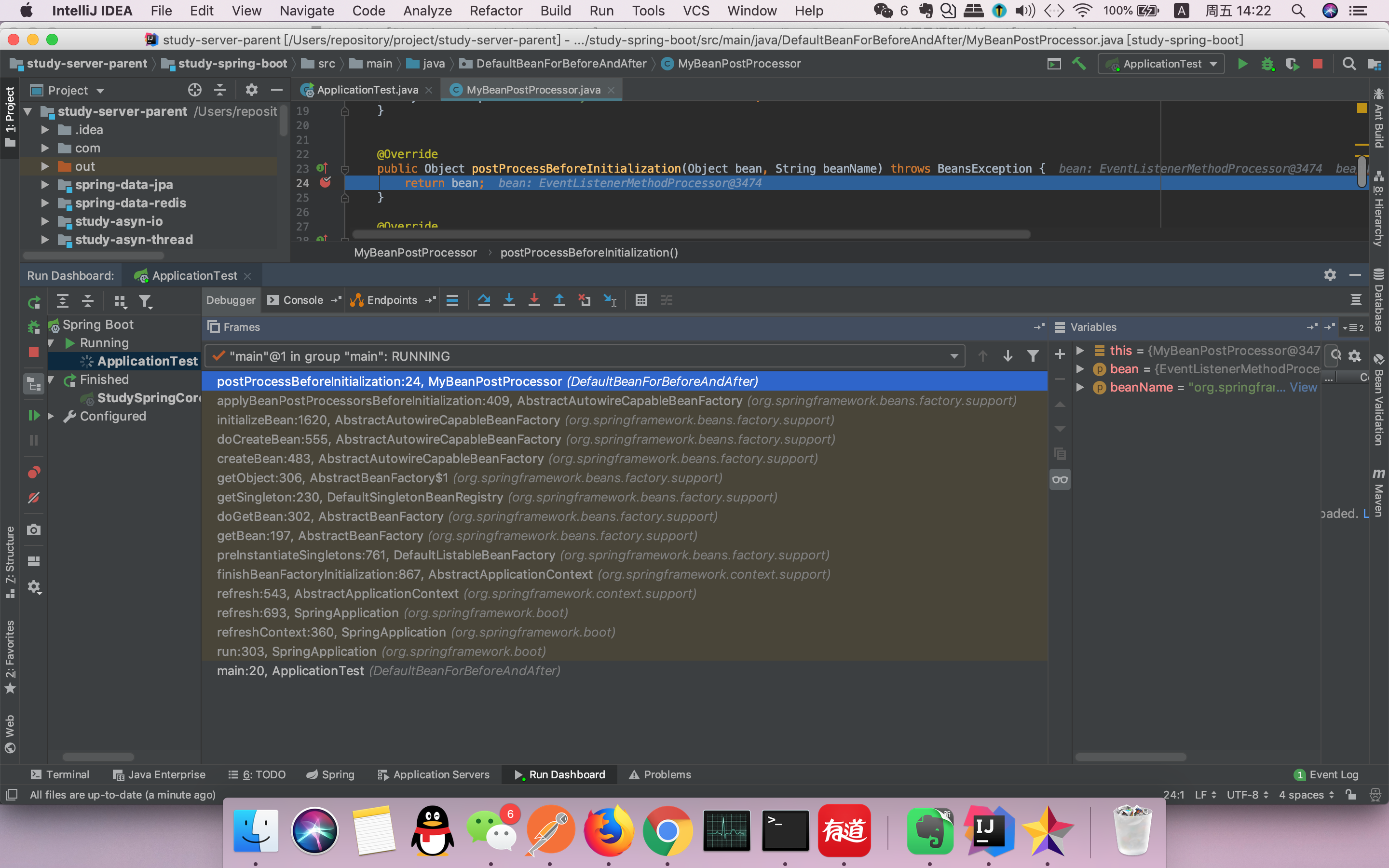
- 是不是非常直观,从 Application 调用入口,到断点 MyBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization 中间的所有调用过程都展示出来了,
那么源码阅读的话就可以按照这个流程逆向进行分析就可以了- 根据调用链可以进入 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.initializeBean 方法中:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
//略...
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
//这里调用了postProcessBeforeInitialization
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
//这里调用了postProcessAfterInitialization
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization 方法:
获取系统中所有的 BeanPostProcessor 对象,并调用其 postProcessBeforeInitialization 方法:
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor beanProcessor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
result = beanProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName);
if (result == null) {
return result;
}
}
return result;
}
applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization
获取系统中所有的 BeanPostProcessor 对象,并调用其 postProcessAfterInitialization 方法:
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor beanProcessor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
result = beanProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
if (result == null) {
return result;
}
}
return result;
}
getBeanPostProcessors(),这里就更简单了,直接获取到 BeanPostProcessor 对象集合。
public List<BeanPostProcessor> getBeanPostProcessors() {
return this.beanPostProcessors;
}
- 根据调用链可以进入 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.initializeBean 方法中:
那么,在什么时候将 BeanPostProcessor 对象都添加到集合中去的呢?
在 Spring 初始化完成后会回调 ApplicationContext 中的 refresh 方法,
在 AbstractApplicationContext 中完成了共通的实现。在 refresh 方法中:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
//略。。。
//从这里注册BeanPostProcessors
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//略。。。
}
}
registerBeanPostProcessors 这里非常简单的调用了 PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate,将 BeanFactory 作为参数传入,那么这里是不是就是可以猜想出是如何获取 BeanPostProcessor 的吧!
protected void registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, this);
}
继续跟入到 registerBeanPostProcessors,这里的第一句代码就很清楚的说明了获取的方式,从 Bean 工厂中获取到所有 BeanPostProcessor 实现类。
public static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) {
String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false);}获取完所有实现类后,根据实现类上的顺序进行排序,然后将排序好的集合对象调用 BeanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor 注册到 BeanFactory 中。这样在 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 中就可以从它的父类 AbstractBeanFactory 中直接获取到 BeanPostProcessor 集合对象了,
也就是上面调用的 getBeanPostProcessors() 方法。registerBeanPostProcessors 方法实现的代码没有什么难度,这里就不多贴代码了。以上代码从 getBean 入口到实际调用 BeanPostProcessor 接口的核心流程分析完毕了。知道了 BeanPostProcessor 执行过程,那么 InitializingBean 的是何时回调的呢?
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.initializeBean 方法中调用 applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization 方法后,调用了 invokeInitMethods 方法。
从方法的实现代码可以看出,如果 Bean 实现了 InitializingBean 接口,就回调 afterPropertiesSet 方法1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);
if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>() {
public Object run() throws Exception {
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
return null;
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) {
throw pae.getException();
}
}
else {
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
}
}
if (mbd != null) {
String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName();
if (initMethodName != null && !(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) &&
!mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) {
invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
}
}这样 BeanPostProcessor 和 InitializingBean 的执行关系如下:postProcessBeforeInitialization→afterPropertiesSet→postProcessAfterInitialization
在 Bean 加载完成后回调中,还可以使用 @PostConstruct 实现。能够实现和 InitializingBean 一样的效果,测试同上面一样
需要在postConstruct对应方法加入断点,可查看方法调用链笔者这里主要阐述下@PostConstruct的原理和代码分析:
@PostConstruct 是通过反射进行调用的。在 InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization 通过反射调用方法。源码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
LifecycleMetadata metadata = findLifecycleMetadata(bean.getClass());
try {
metadata.invokeInitMethods(bean, beanName);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex.getTargetException());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Couldn't invoke init method", ex);
}
return bean;
}这里可以看出,@PostConstruct 其实也是通过 BeanPostProcessor 机制来实现的,
这个可以说是 BeanPostProcessor 使用的一个非常好的例子的。其中 LifecycleMetadata 存储了添加了
@PostConstruct 注解的所有方法,然后通过反射循环调用所有的对应的方法。这里的源码就不继续深究了,有兴趣的可以自行查看下
总结
这里就可以得出 @PostConstruct、BeanPostProcessor、InitializingBean 他们之间的调用关系:
BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization→ @PostConstruct→ InitializingBean→ BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization
既然 @PostConstruct、BeanPostProcessor、InitializingBean 都可以实现在 Bean 初始化完成后执行特定的操作,至于使用哪种还是看项目的使用习惯了,通常来说 InitializingBean 是使用最多的,
@PostConstruct 使用注解的方式来实现的话不够直观,对后期维护来说可能不太适合。
BeanPostProcessor 比较适合在框架类型或者面向特定接口使用。 这里重点还是 BeanPostProcessor,
通过这个接口可以进行更多的业务逻辑操作,至于如何取舍那么就需要看项目的实际情况了
